Machine Learning Potentials and Light-Matter Interaction
Efficient methods for vibrational strong coupling, IR and Raman spectra
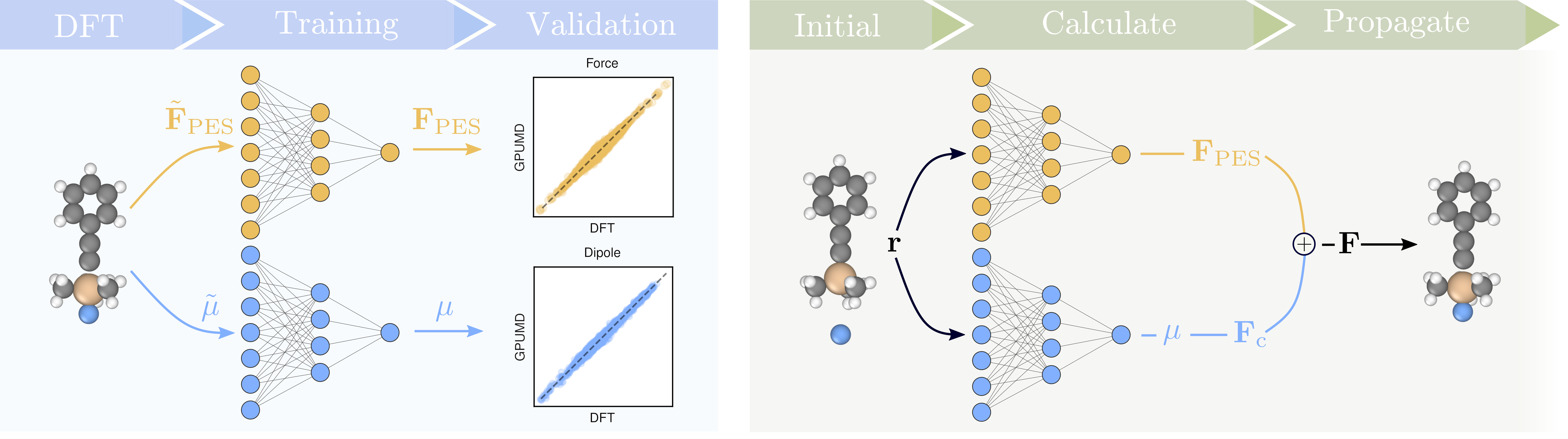
Nuclei stand never still. Every chemical reaction, diffusion, photo-absorption/emission, and relaxation process requires a detailed description of their motion. Machine learning has revolutionized this field over the past years. Modern machine learning potentials can reach near perfect agreement with their reference data (commonly DFT) but are multiple orders of magnitude faster. We train not only for forces and energies, but also dipole moments, polarizabilities, … which paves a way to simulate IR and Raman spectra, describe signatures during chemical reactions, and allows us to describe how chemical reactions can be altered under strong coupling.
Starting point for the interested reader: (Schäfer et al., 2024)
References
2024
- Machine learning for polaritonic chemistry: Accessing chemical kineticsJournal of the American Chemical Society, 2024